RDBMS
Title: NITCbase: RDBMS Implementation Project

Introduction
NITCbase is a Relational Database Management System (RDBMS) implementation project designed to guide undergraduate students through the design and data structures of a basic RDBMS by building one themselves.
- A step-by-step implementation roadmap provides a clear path through various development stages.
- Project documentation includes tutorials that break down concepts, data structures, and design details relevant to each phase.
- Complete design and specifications for the RDBMS and its subsystems are documented and available for reference.
Eight-Layer Design
NITCbase follows an eight-layer architecture, encompassing the core capabilities of a standard RDBMS:
- Table creation and deletion
- Record insertion
- Selection queries
- B+ Tree-based indexing
Supported Operations
The final implementation allows execution of elementary SQL queries:
- CREATE
- DROP
- ALTER
- INSERT
- SELECT
- PROJECT
- EQUI-JOIN
- B+ Tree-related queries (CREATE INDEX, DROP INDEX)
Concurrency Note
Currently, NITCbase does not support concurrent access.
System Components
The eight layers of NITCbase, from bottom to top, are:
- Physical Layer
- Buffer Layer
- B+ Tree Layer
- Block Access Layer
- Cache Layer
- Algebra Layer
- Schema Layer
- Frontend Interface (for user interaction)
High-Level Architecture Diagram
[Insert a link or description of the high-level architecture diagram here]
For a more detailed overview, refer to the project’s architecture page.
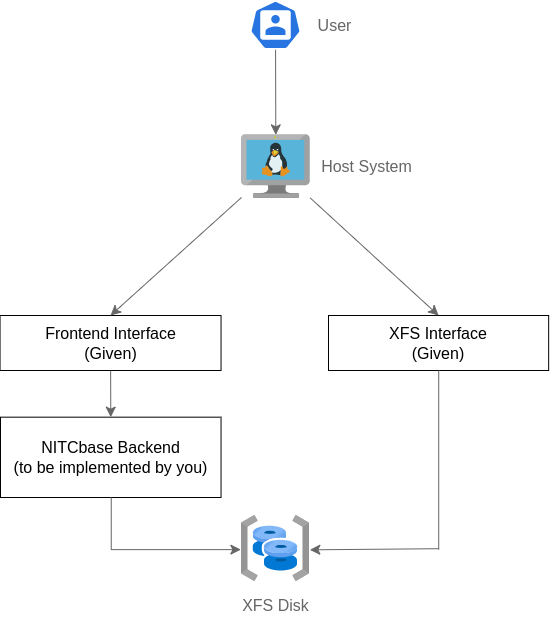
Command-Line Interfaces (CLIs)
NITCbase provides two CLIs:
- Frontend Interface
- XFS Interface
SQL-Like Query Support
Since NITCbase is a relational database, it allows users to execute SQL-like queries on these CLIs.
XFS Disk: Storage Unit
The XFS Disk serves as the single storage unit for all data within NITCbase. It stores:
- Relations (tables)
- Records
- Indexes
- Metadata (for data organization, access, indexing, and modification)
Getting Started
This project is designed for Unix/Linux systems. The documentation details C++ implementation instructions.
Provided Resources:
- XFS Interface: A complete command-line interface enabling users to access the NITCbase disk from the host system (Linux/Unix). It allows operations like:
- Formatting the disk to the NITCbase file system format
- Transferring files between the host system and the NITCbase file system
- Standard NITCbase DDL and DML operations on the database file system
- Disk Class (Disk.cpp): Provides a basic C++ programming interface to the NITCbase disk. Methods include
readBlock()andwriteBlock()for data transfer. - Class Definitions (Intermediate Layers):
- Buffer Layer (StaticBuffer.cpp, BlockBuffer.cpp)
- Block Access Layer (BlockAccess.cpp)
- Cache Layer (OpenRelTable.cpp, RelCacheTable.cpp, AttrCacheTable.cpp)
- B+ Tree Layer (BPlusTree.cpp)
- Schema Layer (Schema.cpp)
- Algebra Layer (Algebra.cpp)
- Documentation provides detailed algorithm descriptions for non-trivial methods in these classes.
- Frontend Interface (Partial Implementation):
- Divided into sub-modules:
- Frontend User Interface (FrontendInterface.cpp) - Code provided
- Frontend Programming Interface (Frontend.cpp) - Only class declaration and functional specifications provided
- Divided into sub-modules:
- Documentation:
- Detailed specification and design of each module
- Database disk organization specification
- System’s high-level user interface specification
- Descriptions of algorithms used in various modules
- Detailed B+ tree operations tutorial
- References to relevant documentation sections for component implementation
- Implementation Roadmap:
- Guides you through system implementation in stages of increasing complexity.
- Each stage builds upon the previous ones and references relevant documentation sections.
- Following the roadmap leads to a fully functional RDBMS implementation.
